DISTRIBUTOR AND SUPPLIER OF
VARIABLE FREQUNCEY DRIVES
VARIABLE FREQUNCEY DRIVES
At Rivera Controls, we offer complete panel solutions for Veriable Frequncy Drives, including designing, engineering, manufacturing and commissioning assistance.

Our Product Range Includes:
- VFD maximum overload 150% of rated current for 60s
- 4 digital inputs
- VFD switching frequency: 3 (default) – 6 – 12– 18 kHz
- VFD Output frequency 0 to 1500Hz
- VFD Accelerate and Decelerate ramps (linear and S type)
- Positive logic control

Our Features include:
- Line Voltage
- Continuous Run Current Rating
- Overload Current Rating
The Basic Of Veriable Frequncy Drives
A variable frequency drive (VFD) is a device that controls the speed and torque of an AC motor by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the power supply. A VFD can also regulate the acceleration and deceleration of the motor during start-up and stop, respectively. A VFD consists of three main components: a rectifier, an inverter, and a control system.
A VFD is used for various purposes, such as:
- Saving energy and improving system efficiency
- Converting power in hybridization applications
- Matching the speed or power of the motor to the process requirements
- Improving the working environment by lowering noise and vibration
- Reducing mechanical stress on the motor and extending its lifetime
- Shaving peak consumption and reducing the motor size required
The Advantages of Veriable Frequency Drives

Energy Saving
A VFD can reduce energy consumption by adjusting the speed and flow of the motor according to the load and process requirements. This reduces the waste of energy and improves the system’s efficiency. For example, in fan and pump applications, which have a variable torque load, reducing the speed by 20% can achieve energy savings of 50%, according to the cube law relationship between speed and power. A VFD can also improve the power factor of the system by reducing the reactive power drawn by the motor.

Increased Reliability
A VFD can increase the reliability of the motor and the system by providing smooth and precise control of speed and torque. A VFD can eliminate the mechanical stresses and shocks caused by direct-on-line starting or stopping of the motor, which can damage the windings, bearings, belts, gears, and other components. A VFD can also protect the motor from electrical faults such as overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, phase imbalance, short circuit, etc. by monitoring and adjusting the output voltage and current. A VFD can also reduce the noise and vibration levels of the motor and the system, which can improve the working environment and extend the equipment lifetime.
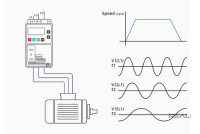
Speed Variations
A VFD can provide a wide range of speed variations for different applications that require variable speed control. A VFD can adjust the speed of the motor from zero to above its rated speed, depending on the load and process requirements. A VFD can also provide a “crawl” speed for maintenance purposes, eliminating the need for additional drives or devices. A VFD can also enable soft starting and stop of the motor, which can reduce inrush current, voltage drop, mechanical stress, and wear and tear.

Soft Starting
A VFD can provide a soft starting of the motor by gradually increasing the frequency and voltage of the power supply from zero to the desired value. This reduces the starting current of the motor, which is normally six to ten times its rated current when started directly online. A high starting current can cause a voltage drop on the supply network, affecting other equipment connected to it. It can also cause winding stress, winding overheating, and insulation damage in the motor. A VFD can prevent these problems by limiting the starting current to a safe level.

Extended Machine Life and Less Maintenance
A VFD can extend the machine’s life and reduce maintenance costs by using a VFD. A VFD can prevent dust, moisture, and corrosion from affecting the motor and the system by keeping them clean and dry. A VFD can also prevent loose connections, faulty cables, and damaged components from causing electrical faults or performance issues by checking and replacing them regularly. A VFD can also reduce the wear and tear of the motor and the system by providing smooth and precise control of speed and torque. A VFD can also monitor and diagnose the condition of the motor and the system by using networking and diagnostic capabilities.

High Power Factor
A VFD can improve the power factor of the system by reducing the reactive power drawn by the motor. Reactive power is the power that is used to build magnetic fields or charge capacitors in the motor but does not contribute to useful work. Reactive power is measured in kVAR and increases the apparent power of the system, measured in kVA. The power factor is the ratio of active power, measured in kW, to apparent power, and indicates how efficiently the system uses power. A low power factor means that more current is required to deliver a given amount of power, which increases losses and costs. A high power factor means that less current is required to deliver a given amount of power, which reduces losses and costs.
Applications of Variable Frequency Drives
Fans: A VFD can control the speed and airflow of fans according to the temperature, pressure, or humidity requirements. This can save energy, reduce noise, improve comfort, and extend fan life.
Pumps: A VFD can control the speed and flow rate of pumps according to the demand or level requirements. This can save energy, reduce wear, prevent water hammer, and improve process control.
Compressors: A VFD can control the speed and pressure of compressors according to load and process requirements. This can save energy, reduce wear, prevent surges, and improve process control. A VFD can also provide soft starting and stopping of the compressor, which can reduce inrush current, voltage drop, mechanical stress, and wear and tear. A VFD can also monitor and diagnose the condition of the compressor and the system by using networking and diagnostic capabilities.
